What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology . Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology.
from byjus.com
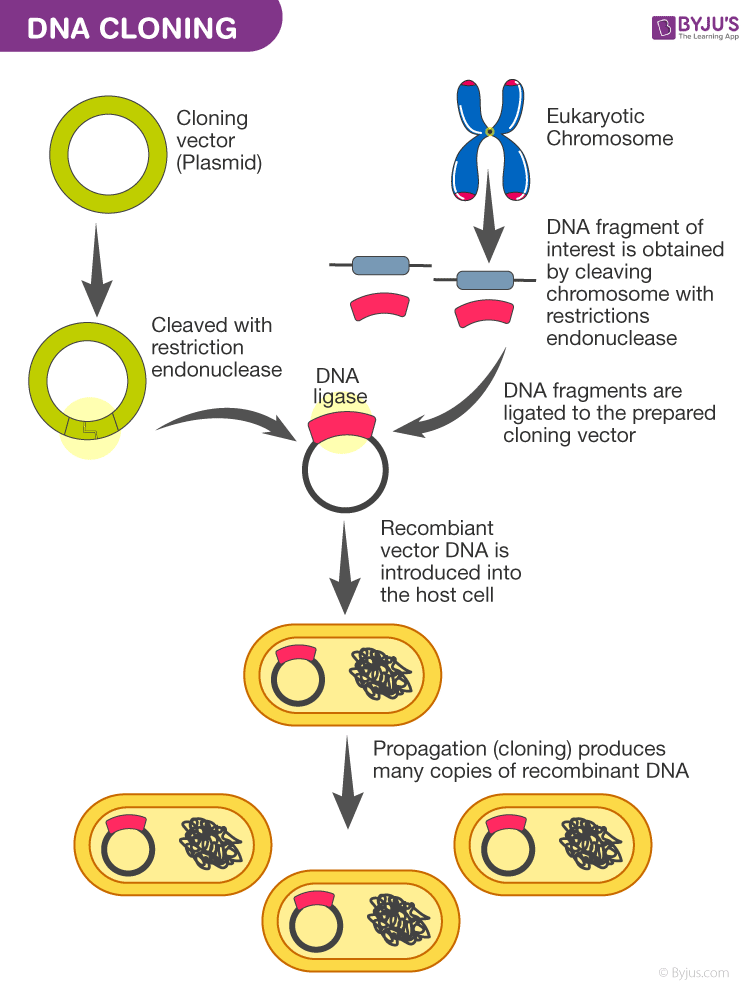
Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through.
Significant Differences between Transformants and
What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. The power of rdna technology.
From www.creativebiomart.net
Protein and Its Expression Systems Creative BioMart What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From leahwhammondz.blob.core.windows.net
Dna Bacteria at leahwhammondz blog What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Explore the science behind. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From vajiramandravi.com
DNA Technology Application, Tools, Process What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology The power of rdna technology. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant dna. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From medium.com
DNA Technology DNA (rDNA) Study Chemistry What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology The power of rdna technology. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce.. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From www.biochain.in
Advantages & Disadvantages of Proteins What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From ireland-blogoneal.blogspot.com
Describe How Dna Technology Could Be Used What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. The power of rdna technology. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From hubpages.com
Production of Therapeutic Proteins HubPages What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From www.biochain.in
What Are The Various Applications Of Proteins? What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From histogene.co
Different types of expression systems of proteins What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Explore the science behind recombinant proteins — from what it is to the types of recombinant proteins — and learn how they are. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Recombinant dna is. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From animalia-life.club
Examples Of Modified Crops What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna,. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From bio.libretexts.org
12.1 Microbes and the Tools of Engineering Biology LibreTexts What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Explore the science behind. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From byjus.com
Significant Differences between Transformants and What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host cell. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal biotechnology. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through.. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From www.youtube.com
Protein Expression in Ecoli YouTube What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant proteins are. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From walteredean.blob.core.windows.net
Dna Technology Protein Production at walteredean blog What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Recombinant proteins are commonly used to produce. Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant proteins are formed by. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From www.mdpi.com
Biology Free FullText Implementation of a Practical Teaching What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Recombinant dna (rdna) technology has resulted in breakthroughs in crop and animal. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From plantlet.org
Gene Cloning Basic, Requirements & Steps Plantlet What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From bhavinbiology.blogspot.kr
Biology The Study Of Life DNA Technology What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant dna, molecules of dna from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science,. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. The power of rdna technology. Explore the science behind recombinant. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
3 approaches to vaccine antigens. Protein antigens are What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology Recombinant proteins are proteins that are genetically engineered in laboratories by inserting the gene encoding the protein of interest into an. The power of rdna technology. Recombinant dna is a molecule of dna that has been modified to include genes from multiple sources, either through genetic recombination or through. Recombinant proteins are formed by transfecting foreign genes into a host. What Does Recombinant Protein Mean In Biology.